Semiconductor an Introduction
There are few semiconductor materials which conductivity is around 10-4 ohm-m to 0.5 Ohm-m at normal ambient temperature. But materials are also having resistivity in this range. But a very important criteria that actual semiconductor materials are negative temperature co-efficient of resistance and act as insulator in absolute 0°K temperature. These materials are called as semiconductor. There are few some semiconducting materials are popularly used.
- Silicon
- Germanium
- Corbon
- Gallium Arsenide
- Selenium
- Cadmium sulphide
In above listed silicon are germanium are mostly used.
Structure of Silicon Atom
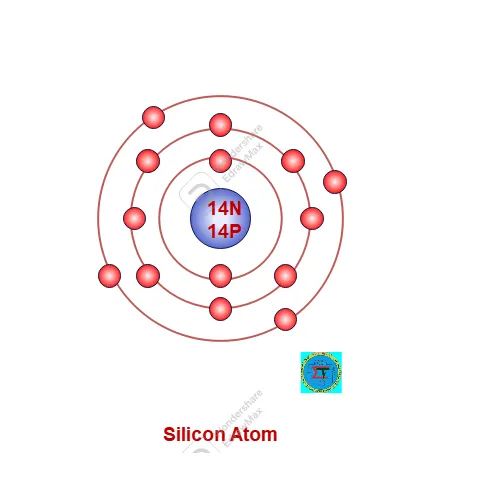
A silicon atom consists 14 protons in nucleus and 14 electrons are possessed in orbit around nucleus as per 2n2 rule. Along with 14 neutrons also available in nucleus.
Atomic Number of Silicon Atom =14 electron = 14 proton =14
Atomic Mass of silicon atom = 14 proton +14 neutron= 28
Electronic configuration as per 2n2 rule as follows,
First Orbit (n1) = 2x 12 = 2
Second Orbit = 2x 22 =8
Third orbit is valence orbit filled with remaining 4 electrons.
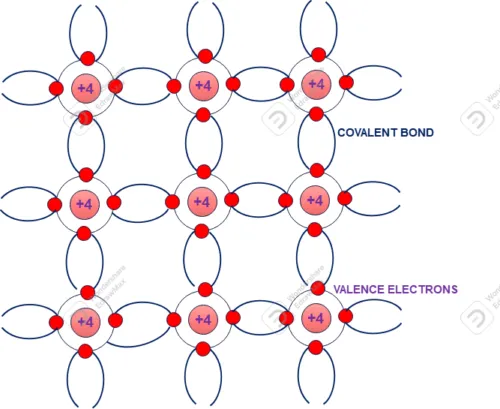
A silicon atom has crystalline structure (see figure) and each surrounded by four atoms. Valance electrons of each atom made covalent bond with surrounded atom. In normal room temperature in made strong covalent band which need more energy to break it. As all valance electrons are shared with surrounding atom making by covalent bond no free electrons are available. Hence it is almost act as insulator.
Structure of Germanium Atom
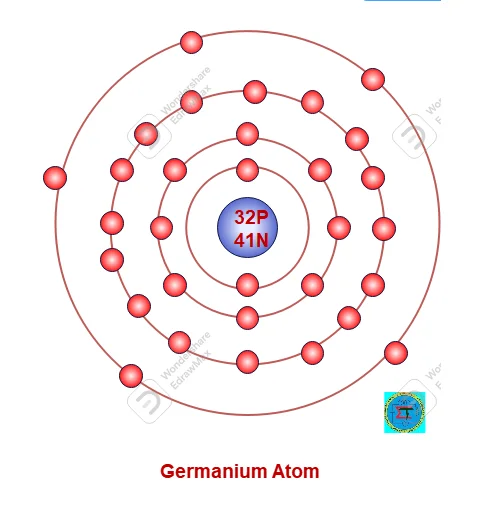
A Germanium atom consists 32 protons in nucleus and 32 electrons are possessed in orbit around nucleus as per 2n2 rule. Along with 41 neutrons also available in nucleus.
Atomic Number of Germanium Atom =32 electron = 32 proton =32
Atomic Mass of Germanium atom = 32 proton +41 neutron= 73
Electronic configuration as per 2n2 rule as follows,
First Orbit (n1) = 2x 12 = 2
Second Orbit(n2) = 2x 22 =8
Second Orbit(n3) = 2x 32 =18
Third orbit is valence orbit filled with remaining 4 electrons.
A Germanium atom has crystalline structure (see figure) and each surrounded by four atoms. Valance electrons of each atom made covalent bond with surrounded atom. In normal room temperature in made strong covalent band which need more energy to break it. As all valance electrons are shared with surrounding atom making by covalent bond no free electrons are available. Hence it is almost act as insulator
Comparison of Silicon and Germanium Atom
| Particulars | Silicon | Germanium |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 14 | 32 |
| Atomic Mass | 28 | 73 |
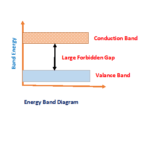
| Forbidden Energy gap | 1.12 eV | 0.72eV |
| Location of valence electron | In Third orbit | In Fourth orbit |
| Temperature sensitivity | Less | More |
| Application | Power Electronics | Transistors, fluorescent material |