Introduction
Some certain materials are behaves in between conductor and insulator. These materials are called as semiconductors. Its resistivity measure between insulator and conductor.
There are few popular semiconductor materials are widely used world wide
- Silicon
- Germanium
- Carbon
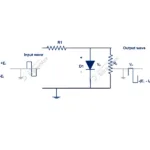
These semi conducting materials are mostly used to develop various electronic components such diodes, transistors, DIAC. TRIAC, MOSFET etc. which used in every electronic devices.
Properties of a Semiconductor.
A semiconductor property studied by its electrical conductivity characteristics. Its resistivity about 0.0001 Ohm to 5 milli Ohm. Its conducting state between conducting and insulator. Every semi conductor atom consists four valence electron and made with covalent bond with adjacent atom. Due to these configuration a semiconductor almost act as insulator. So necessary effort to be applied to break these covalent bond to bring conducting state. Hence it is doped ( adding some other material) with it , it used effectively as there are free electrons or holes increased.
This availability of electrons and its deficiency decided by nature of doping material used.
Almost silicon and germanium are widely used for making electronic components.
Pure semiconductor which not doped called as intrinsic type, On other hand doped called as extrinsic type.
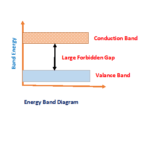
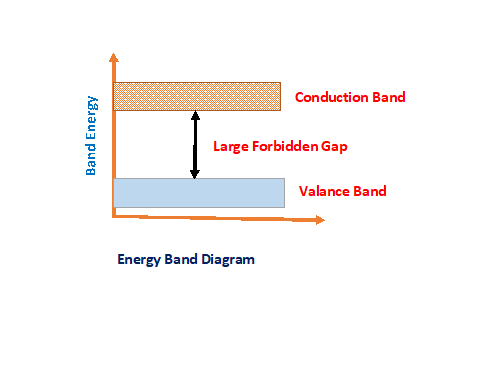
Every material’s conducting nature decided by forbidden gap ( energy gap between valance band and conduction band)
In conductor there is no forbidden energy gap and insulator it more. But a semiconductor forbidden energy gap in between is nearly equal to 1 electron volt (eV). For germanium and silicon it is equal to 0.7eV to 1.1eV. Hence it is relatively very less energy required to overcome forbidden energy gap. All semiconducting materials are temperature sensitive. It has negative temperature co-efficient characteristics.
While increase of temperature some semi conductor breaks covalent band emits free electrons. As same as decrease of temperature or equal to room temperature it act as insulator.
Characteristics of a Semiconductor
- Its resistance lies between insulator and conductor
- It is negative temperature co-efficient
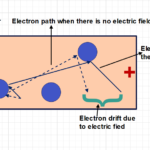
- current circulation carried out by free electrons
- Pure semiconductors are insulator in nature. while adding some impurities like gallium, arsenic, prosperous, aluminum its conducting property considerably increased.
- Each semi conductor atom formed covalent bond with adjacent four atoms.
Applications of semiconductor
- Fabrication of electronics devices like amplifiers, television, cameras
- Fabrication of sensors
- Mobile communications, satellites and radars, Navigation equipments
- Fiber optical devices