Since, earlier years various type of atomic models are demonstrated by scientist according to their experiment in atomic physics, Let see about that various model of atomic structure here.
- John Dalton’s model
- Plum pudding model
- Rutherford’s model
- Bohr’s model
1. John Dalton’s Model

Jhon Dalton is an English scientist who demonstrated his first atomic model atom in atomic physics research. According to his research,
- Each element in the universe made up by a tiny particle. These particles called as Atom.
- Either an Atom is indivisible of indestructible. Because it is a very basic particle in nature.
- All these particles have identical physical and chemical properties.
- These Atom making a group or compounding to create a different kind of element. These elements also called as molecule.
Even he has contributed best model to improve atomic research in future, there were some drawbacks too,
- Atom of same elements are similar in all respects and different elements have different in all respects.
- But few other scientists discovered that an atom containing three different kinds of particle into it. They called as proton, Electron and neutron.
2. Plum pudding model
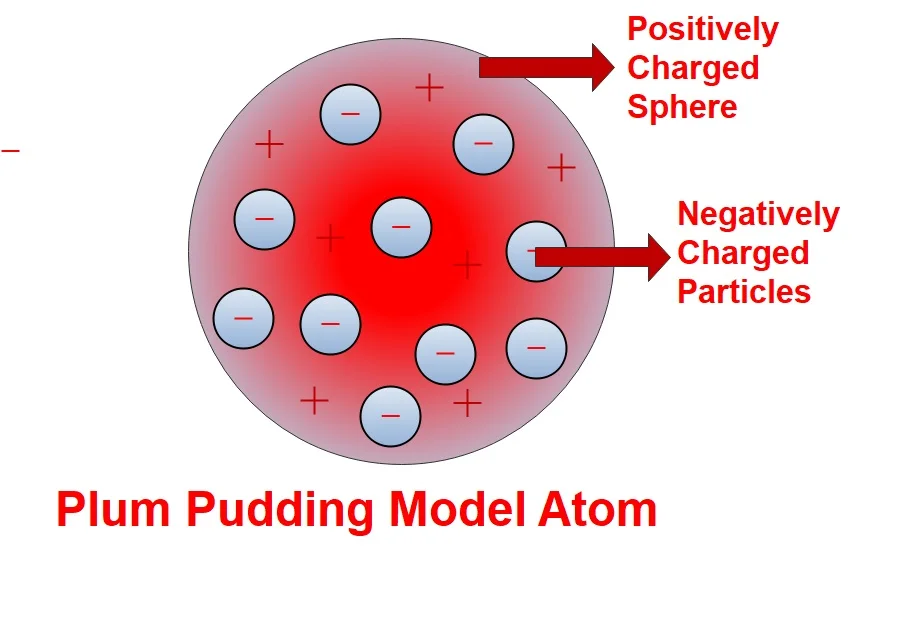
After Electron discovered in 1987, Scientist have thought an Atom is divisible further, it has more sub particle into it. During the period the scientist J.J Thomson (in 1904) released his atomic model to the world. According to his research an atom has shape like a spherical pudding plum cake. The famous model demonstrated by him called as Plum pudding model. This model was explained as it consists sub particles called as Electronics negatively charged. But this model did not explain about nucleolus of an atom. But this atom has positive charges are released by sphere which is equal magnitude of negative charge existence in the atom. This cause neutralizes an atom and keep in stabled manner.
Even it has upgraded atomic model to compare with Dalton model, it fails to explains about how positive charges are balances with negative charged electrons to maintain stability of an atom.
3. Rutherford’s model
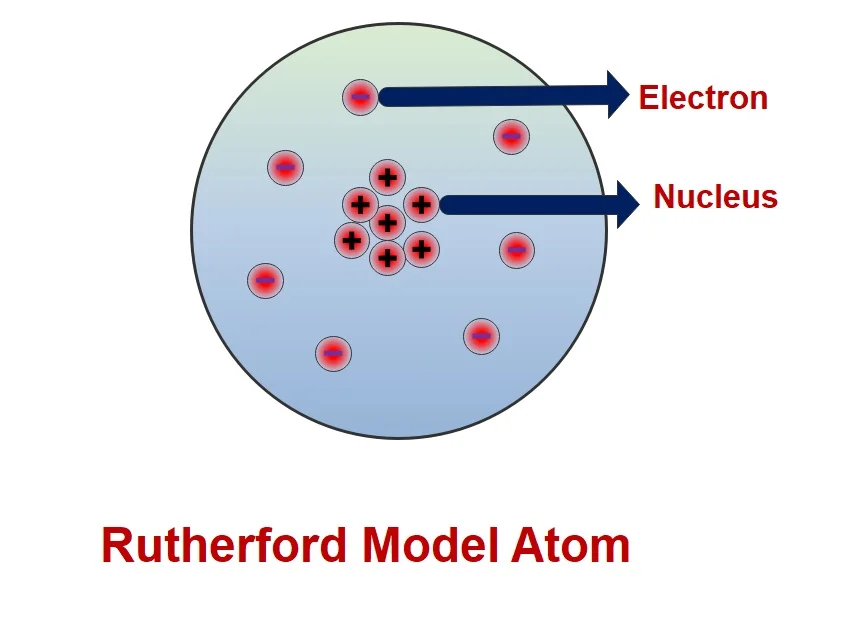
Rutherford proved that J.J Thomson model was incorrect as it failed to explain about nucleus of an atom. Because during his experiment, he used to scatter α- particle on a gold sheet. He observed that most of α- particle passed through gold sheet. But some α- particlescattered in 180-degree angle. So, Rutherford concluded that there is a some positively charged particle available in a place which responsible to scatter α- particle.
Rutherford has demonstrated atom that containing a nucleus in center part of an atom. The nucleus having small volume and consists high central charge. Further this center volume of an atom whole responsible for mass of an atom. This center part of an atom called as nucleus of an atom. In addition to an atom containing light weight particle which is surrounded in this nucleus called as Electrons. These Electrons revolving in a certain path around nucleus. This path called as Orbit. His model sometimes called as planetary atomic model of atom.
4. Bohr’s model
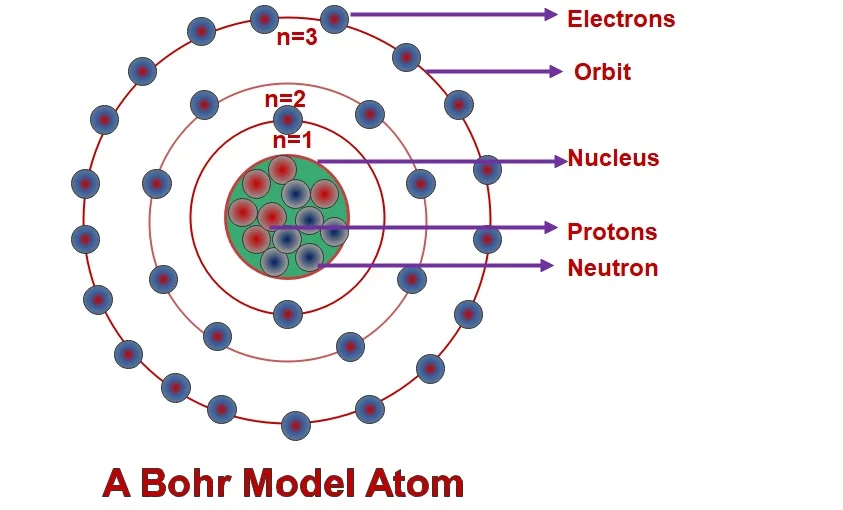
Bohr atomic model was released by Neil Bohr in 1915.
This atom model demonstrated based on modified Rutherford model. Let say, it is an upgraded of Rutherford model. As per Bohr’s model he explained that he explained that each Electrons in an atom has a certain energy level.
Assumption of Bohr’s Atomic model
- An Atom containing three sub particles called as proton, Electron and neutron.
- Each atom containing a volume of mass in its center part of an atom is called as nucleus.
- Protons and Neutrons are in stationary state in the nucleus.
- Electrons are revolving around nucleus in a certain path is called as nucleus.
- Protons, Electrons, Neutrons are containing positive, negative, zero charges respectively.
- Electrons are revolving in orbit without losing energy.
- Each orbit stationary states as circular paths on which the angular momentum of the electron is an integral multiple of h/2πas defined by Bohr’s Quantization principle λ =h/mv.
Where,
h- Planck Constant.
Λ- Wave length of the matter.
v- velocity of the electrons.
m- mass of the electrons
- Electrons are stabled in a particular orbit by attractive force with nucleus and repulsion force between electrons.
- Each orbit electrons are containing different kind of energy levels. Each orbit is in an integer number called as n = 1,2,3,4,5……
- Each orbits containing electrons according to 2n2 rule where” n” is orbit number.
| Orbit Number | Number of Electrons |
| N=1 | 2 |
| N=2 | 8 |
| N=3 | 18 |
| N=4 | 32 |
| N=5 | 50 |
| N=6 | 72 |
| N=7 | 98 |
Electrons are shifting lower state of energy levels to higher state of energy levels by gaining energy and higher state to lower state to lower state by losing energy.