Torque is an important characteristic in a motor developed in the rotor while applying external voltage to its stator. It mainly causes to rotate the rotor in the angular direction. Before we go to analyze about torque equation, we should know about what is torque in the motor.
Torque – Definition:
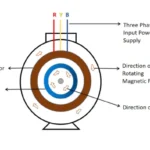
Torque is an angular force exerted in rotor, by rotor current. The rotor current will be generated due to applying external applying voltage to the rotor and principle of electromagnetic mutual induction.
Unit of the Torque: N -m
This torque generated in motor , is merely depends on following three factors
- The rotor power factor under running condition (CosØ2R)
- The rotor current under running condition (I2r)
- The part of rotating magnetic field (or) Emf of the rotor which induces rotor current in the rotor.
With above conclusion, torque may be mathematically expressed as.
TαØ I2r CosØ2R
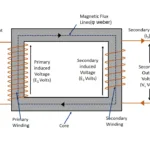
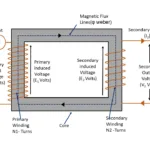
From above equation , the Ø – rotating magnetic field is commonly connected between stator and rotor. Further it is depends on input voltage to the motor .i.e E1
∴ Øα E1
As we know that E2/E1 =K
E2 = Secondary/ Rotor induced Emf
E1 =Primary/ Stator applied voltage
So, It can be re-written as E2 α E1
E2 α E1 α Ø
The rotor current flowing through it can be determined by using below equation
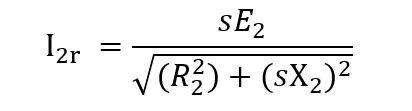
The rotor power factor under running condition
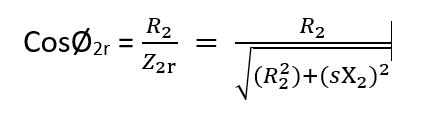
Let substitute Both equation of Ø, I2r and CosØ2r , we get
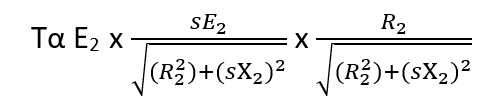
By simplifying above equation, we get torque equation of an induction motor
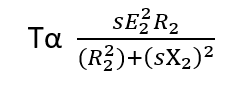
This equation generally known as torque equation of an induction motor.
Torque Equation of an induction motor
By using a constant proportionality factor K, the equation can be re-written as
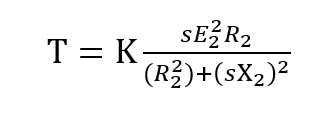
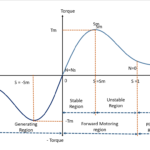
The torque is important key factor to drive load by an induction motor