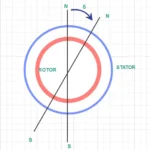
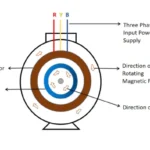
This article will explains about slip frequency and induced emf in an induction motor. When three phase supply applied to stator winding of an induction motor, rotating magnetic field induced. This magnetic field rotating in a speed is called as synchronous speed. The magnetic flux lines produced by RMF cuts by rotor winding conductor and there is an EMF induces which causes the circulation of rotor current. The magnetic field induced in rotor opposes which causes to generated. So there is a relative velocity generated. This relative velocity tends to rotate the rotor is same direction of the rotor.
Slip Frequency (or) Rotor Frequency
Now the subject about the frequency will comes in discussion. The supply given to stator winding shall be F Hz. So the same frequency should be generated in rotor. No! it is not correct in this case. The frequency generated in rotor winding vary between F Hz to 0 Hz according to relative velocity. In other terms value of slip in between stator and rotor.
Rotor frequency Fr = sF Hz
When motor is in standstill N = 0 , S = 1
At motor stand still , rotor does not rotates. So slip becomes 1
Rotor frequency Fr = sF Hz =
= 1 X F
Rotor frequency at stand still Fr =F Hz
hen motor is in rotating at maximum speed N = Ns , S = 1
At motor stand still , rotor does not rotates. So slip becomes 0. as well as there is no relative velocity (Under consideration of ideal induction motor)
Rotor frequency Fr = sF Hz =
= 0 X F
Rotor frequency at stand still Fr =0 Hz
As above statements shows frequency is directly proportional to the slip, it is also called as slip frequency
Induced Emf in the rotor winding
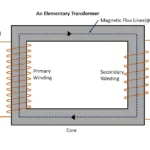
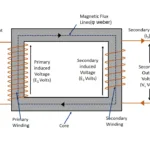
An induction motor alternatively known as rotating transformer. Its stator winding and rotor winding are act as primary and secondary winding respectively. Therefore using equation of transformation ration
[latextpage]
![]()
N1 and N2 are shows stator winding turns
E1 and E2 are shows Stator and rotor induced Emf per phase
This equation is applicable only, when rotor is in stand still condition
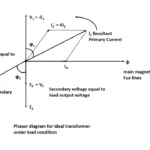
When rotor is starts to accelerates , The relative velocity between rotor and stator starts to reduces. In other words slip reduced from S=1 towards S =0 (approximately). This reduced relative velocity (or) slip tends to reduce induced emf in rotor winding. Let us consider Emf induced under running condition as E2r . As taking ration between E2 and E2r
![]()
![]()
![]()
So,
Emf induced at stand still Er = E2 when Slip (s) =1 and rotor RPM N =0
Emf induced during actual running of motor E2r = sE2 when Slip (s) >1 and rotor RPM in between N =0 and N =Ns
So this article conclude about slip frequency and rotor induced emf in an induction motor stand still as well as under running condition.