As we know that resistance is a property which oppose to flow electric current through a material. But it is important to note that each material does not offer same value of resistance to flow of electricity. Definitely it differs from one material to another material.
So study has been carried out on each material about its resistance in a unit dimension of it. according to study it found that
” Resistance offered by one unit cross section of material is directly proportional to length (L) of it and inversely proportional to cross section area (A) of it”
R α L
R α 1/A
Combining above equation we get,
R α L/A
Bu substituting ρ (specific resistance ) the equation can be written as
R = ρ ( L / A )
R = Resistance of a material in Ohms
ρ = Specific resistance or resistivity in Ohm -Cm
L = Length of the material in cm
A = Cross section of material in cm2
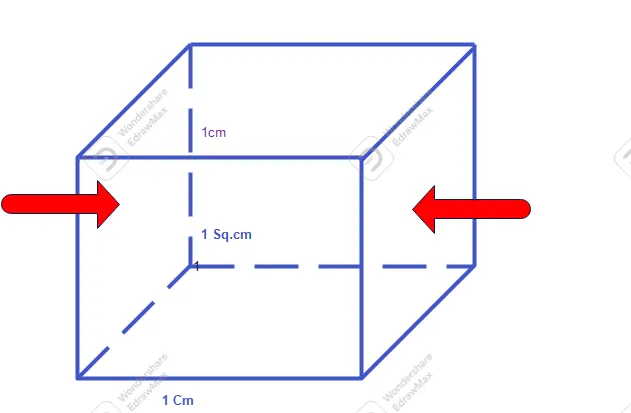
Definition of Resistivity
Resistivity or Specific resistance of a material is defined as resistance offered while it having unit length and per unit cross sectional area dimension.
Unit of Resistivity = [( Unit of Area (A) x (Unit of Resistance (R)] / Unit of Length (L)
The below table shows important materials,
| Sr.No | Material Name | Specific Resistance in Ohm -Cm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Copper | 1.7 x 10-8 |
| 2 | Iron | 9.68 x 10 -8 |
| 3 | Nichrome | 100 x 10 -8 |
| 4 | Glass | 1010 to 1014 |
| 5 | Rubber | 1013 |
| 6 | Silver | 1.6 x10-8 |
| 7 | Aluminum | 2.65 x 10-8 |
| 8 | Tungsten | 5.6 x 10-8 |
| 9 | Constantan | 4.9 x 10-7 |
| 10 | Mica | 1011 to 1015 |