Electrical sources in a very important component in an electrical network. It is responsible to deliver required electrical energy to networks. A electrical networks contains several kind of sources. Sources used in an electrical network either dependent or independent.
Independent source is called as convert one kind of energy (mechanical, light, chemical) into electrical energy.
Example: DC Generators, Alternators, Cells and Batteries
Dependent sources are need electrical energy, further convert it in desired form of electrical such current, voltage or a particular waveform
Example: Timing circuits, Oscillators, other frequency encountered circuits.
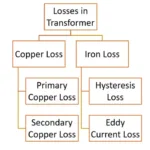
According to its electrical characteristics sources classification of energy sources refer below flow chart.
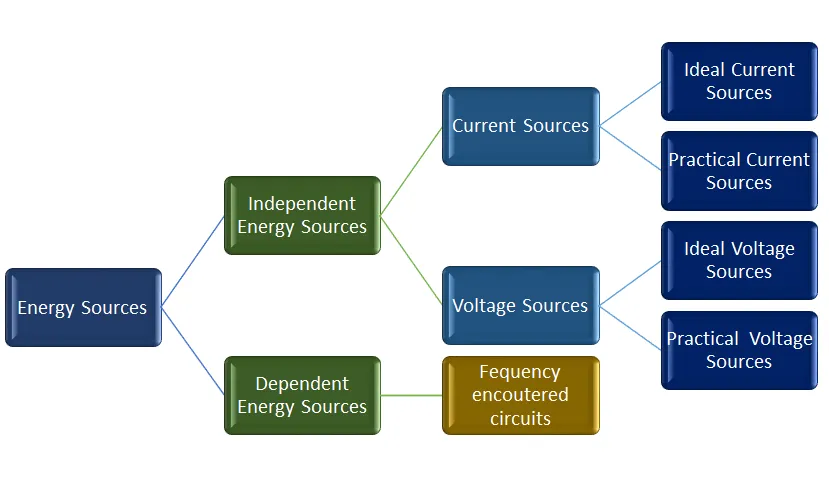
However dependent energy source is also available in a circuit, it is most important to study about independent sources,
With reference of above flow chart independent voltage sources are below listed,
- Independent voltage source
- Ideal voltage source
- Practical voltage source
- Independent current sources
- Ideal current sources
- Practical current sources.
I. Independent Voltage Source
A voltage source is defined as deliver energy to network with specified terminal voltage, while irrespective of magnitude of current flowing through it. As name says it is important condition is to maintain voltage in circuit.
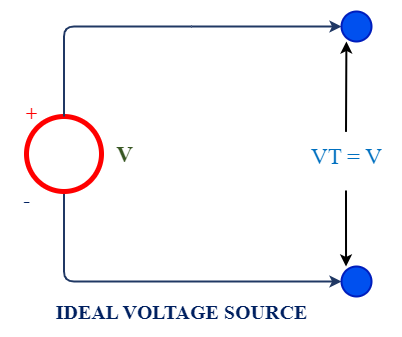
1. Ideal Voltage Source
A voltage source which terminal voltage remains always constant if any values of the current supplied to circuits. Its voltage does not change while increase or decrease magnitude of current. Obviously it does not contain any internal resistance into it.
For example, an ideal voltage source having 50V capacity will provide always constant if 1A, 2A or 10A current flowing to circuit. It is represented as circle diagram and positive and negative polarity are denoted in it for identification of output supply polarity. It does not contain any internal resistance. Please refer below figure.
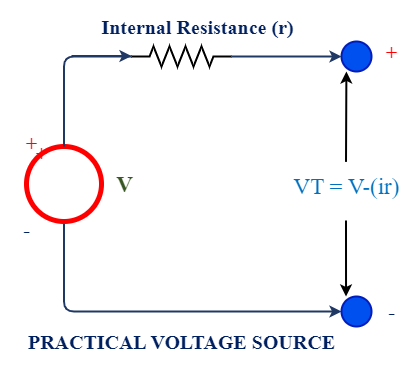
2. Practical Voltage Source
A practical voltage source output voltage changes with proportional to the output current flowing in circuit. Because of it is having an internal resistance (Rse) connected in series, causes few amount of voltage dropped in it and remaining voltage available in its terminal.
However, a good practical source has very small amount of internal resistance (Rse), so voltage drop will not be more.
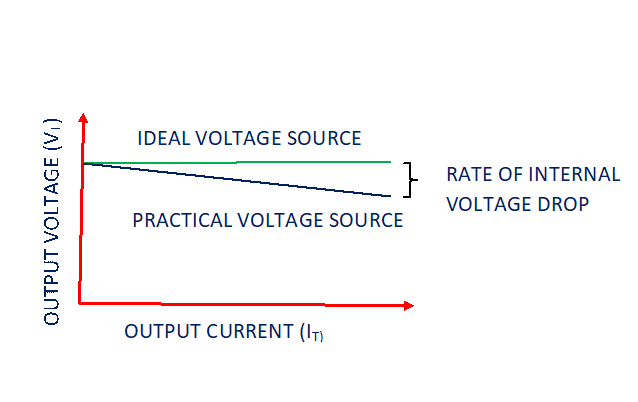
A practical voltage source always ideal voltage source when it is open circuited. But when current flows, few voltage drops in series internal resistance (Rse). Its characteristics shows output voltage curve in inclined due to internal voltage drop. Please refer below graph.
Output Voltage (VT) = V- ir
II. Independent Current Source
A current source defined as deliver energy to circuit with specified amount of current through its load terminal. There may be any amount of voltage in its terminal.
However, it is need to satisfy current requirement to circuit. Its main objective is maintaining current in the circuit.
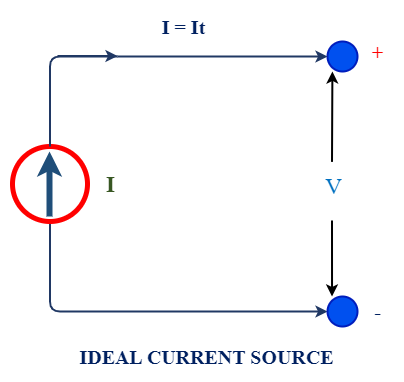
1. Ideal current source
An ideal current source assumed that which can deliver constant magnitude of current in network with irrespective value of load connected across its terminal. Its current magnitude never changes with change in load resistance. Obviously it contains zero shunt resistance. A shunt resistance is known as path to divert desired amount of current.
For example, a 10 ampere current source will deliver constant 10A current in any changes of load resistance such 10 ohms, 20 ohm or 100 ohms. It is represented as circle diagram with arrow showing direction of current flow from source.
Practical Current source
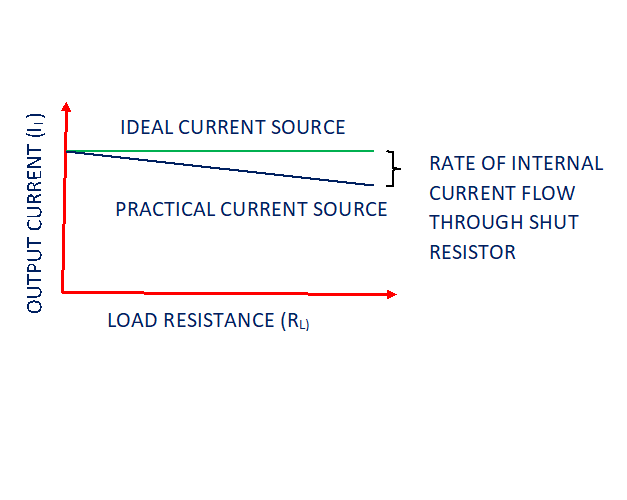
A practical current source has characteristics that output current falls considerable amount while changes in load resistance. A practical current source contains shut resistance connected across it responsible for drop in output current.
When load resistance increases current flows through shut resistance increases. So output current falls. Hence it is very important to keep internal shut resistance must be kept high for getting maximum output current.
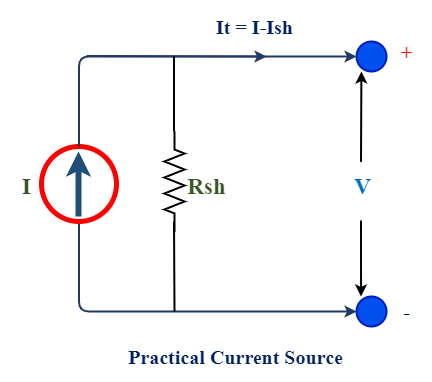
Equation for output load current (It)= [Vo/Rse+Rl] x I
Since above equation shows that Rsh>> RL then I=IT.
If source internal shut resistance is much larger than external load resistance , it can deliver current equal to ideal current source.


Nice Article!!