Introduction
Atom is a Greek word which means “it is indivisible further”. Universe made with variety kind of atom in nature. Atom is a smallest particle exists in every element. According to combination of elements it creates different kind of material depending on physical and chemical properties of an Atom.
Structure of an Atom
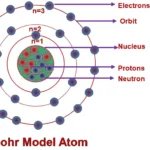
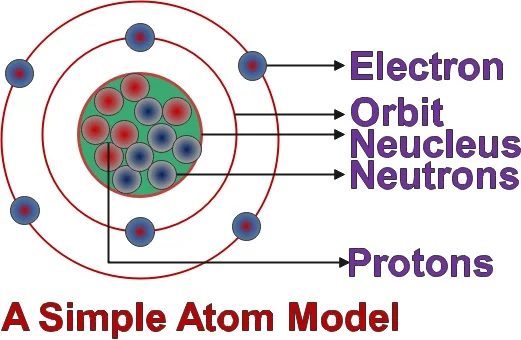
An atom is an smallest particle which contains nucleus in its center parts and electrons are revolving around its orbit. Nucleus contains protons and neutrons into it. Protons are having positive charge and electrons are having negative charge. But neutron do not have any charge. Each orbit around nucleus are formed with certain number of electrons. these count of electrons are decided as 2n2, where n is orbit number.
Properties of an Atom
An Electron is a smaller and light weight particle in an Atom. Electrons are fundamental particles. They don’t contains ay sub particles. The mass of the electrons is about 1/2000 the mass of proton. Electrons are negatively charged particle and have electrical charge -1. Unlike protons and neutrons, it rotates in particular path called as orbit.
Protons are found in nucleus of an atom. It is a dense particle having mass of 1.67 times of neutrons. Protons are positively charged particle and having electrical charge +1.
Neutrons do not have electrical charge. Its mass about 1 amu.
Atomic Number
Atomic number of an atom defined as either it is number protons or electrons existing there. In most cases it is defined as atomic number is equal to the number of protons available in the nucleus.
Atomic number = number of protons in nucleus =Number of Electrons in orbit
Z=P=E
For Example,
A hydrogen atom has shown in fig containing one electron in its orbit and one electron in its orbit.
Atomic number of hydrogen atom = 1 =1
So, Atomic Number of Hydrogen atom=1.
Z=1
Let see one more example,
An Oxygen atom has shown in fig containing eight electrons in its orbit and eight protons in its nucleus.
Atomic number = number of protons in nucleus =Number of Electrons in orbit
Atomic number of an Oxygen atom= 8=8.
Z=8.
Atomic Mass
Atomic mass number of an atom defined as it is protons and neutrons available in the nucleus.
Electrons has negligible mass. Hence it has omitted.
Atomic Mass = Number of protons + Number of Neutrons.
It has denoted by A.
A=P+N.
For example, an Oxygen Atom shown in fig having 8 protons, 8 Electrons, 8 Neutrons.
Hence atomic mass number = Number of protons+ Number of Neutrons
A = P+N
A=8+8
A=16.
Let see one more example. A carbon atom containing six protons, six Electrons, Six Neutrons.
Hence atomic mass number = Number of protons + Number of Electrons.
A=6+6
A=6