Effect of the heat in semiconductor
When conductor heated by external source, the atoms are situated in the fixed locations, tends to vibrate. This vibration causes release the free electron from an atom which movement in surrounding mass of the electrons. This causes reduction of the flow of electron, that constitute current. The reduced electron means resistance of the conductor increased. Such conductor known as positive temperature co-efficient. The resistance increases due to increases the temperature.
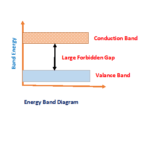
A pure semiconductor i.e. an undoped semiconductor at absolute zero (-273°C) temperature does not have free electrons. So, it acts as a perfect insulator. Because there is no electrons or holes are present in the valance band.
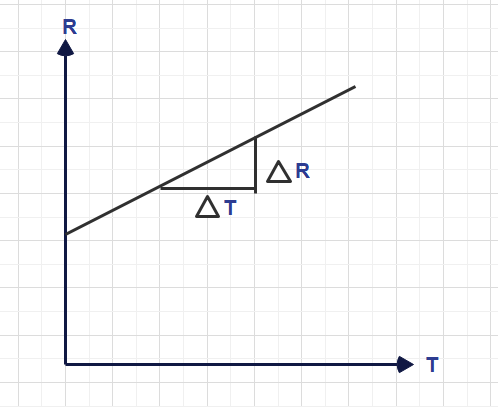
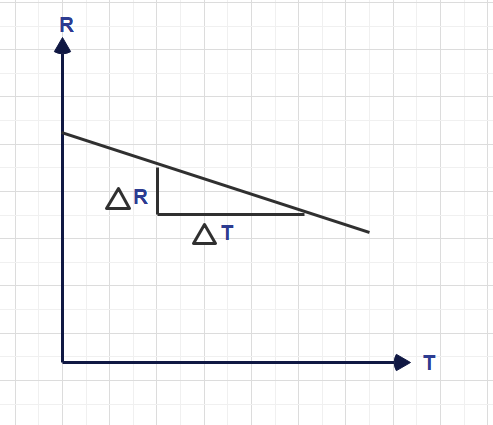
Note that a semiconductor behaves as insulator at absolute zero (-273°C) temperature
When temperature increases in the semiconductor electrons are break away and jumps to conduction band from covalent band. So, it creates holes in the valance bond and free electrons in the conduction bond. It allows current conduction due to creation of holes and valance electrons (or) movement of holes electrons pair by electron movement. The rate of electrons, holes pair depends on rate of increasing thermal energy provided to semiconductor atom.
Note that, Semiconductor has property of negative temperature co-efficient.
However, generation of free electrons occurs in a semiconductor is comparatively lower that pure conductor. The thermal generation is semiconductor is a much dominating factor and need to be avoided in practical application. Because semiconductor current increases with increases in temperature, which totally independent and cannot be controlled by external devices.
A heavily doped conductor almost acts as a conductor, and widely used for practical applications.
Effect of the Light in the semiconductor
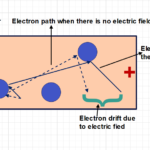
Like thermal energy causes generation of the holes and free electrons in the semiconductor, using light source also electrons-holes pair can be created. A semiconductor material has few free electrons in conduction bond, when it is not illuminated, it offers resistance to flow of these electrons called as dark resistance. As same as using thermal energy, when semiconductor material illuminated by external source, few electrons are break away from valance bond to conduction bond. Hence their electron-holes pairing happens as long as it is illuminated by external light source.
Typical Quantities in semiconductor atoms in absolute Zero temperature
| Particulars | Silicon | Germanium |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Density (Per cm3) | 5 x 1022 | 4.4 x 1022 |
| Electron density (ni) | 1.5 x 1010 | 2.5 x 1013 |
| Electron mobility (uo) (cm2/V.s) | 1500 | 3800 |
| Hole mobility (up)(cm/V.s) | 500 | 1800 |