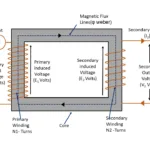
Capacitor a static electrical device used to store electrical energy for short time. In general capacitor made with two electrodes and a dielectric insulating medium kept between those electrodes. There are various type of material used as dielectric medium. Each makes different effect in capacitance and accumulating charge in a capacitor. Here we shall discuss about characteristics of dielectric materials behaves in a capacitor
In Vacuum medium
Let consider two parallel plates are connected across a potential difference ‘V’ and kept in a vacuum chamber. As there is no other material used between these plates vacuum act as dielectric medium. On apply of potential difference between both plates, they will become positive and negatively charged (Q0) with uniform electric intensity.
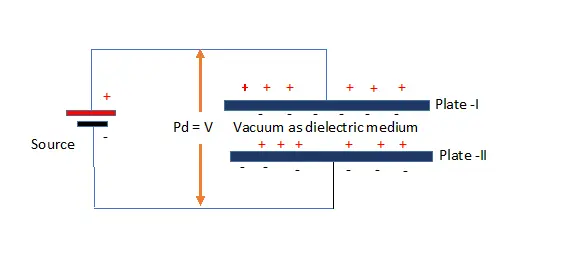
There will be uniform field intensity maintained,
Electric field intensity in parallel plates (E) = V/d Volts/metre
![]()
The magnitude of charge accumulated is proportional to applied voltage between plates.
Q0 = V
Q0 =C0 V
where
Q0 = Charge accumulated in vacuum
C0 = Capacitance when vacuum used as di electric medium
On application of Gauss theorem, it states that electric flux in a closed surface is proportional to net electric charge in that surface (Q) and 1/ , where is known as relative permittivity of free space.
Electric Flux (D) =Q/ε0
Electric field strength and flux density are related to each other
D = ε0E
(or)
The field strength between plates (E) = D/ε0
Electric flux density (D) =Q/ε0 x 1/A = Q/ε0A
Since V = Ad capacitance of plates given as Q0 =ε0 A/d
where ε0 is absolute permittivity in the free space expressed in farads /metre
Absolute permittivity in free space =8.85 × 10-12
When dielectric medium introduced
Now let consider that some dielectric material is introduced between both parallel plates of capacitor.
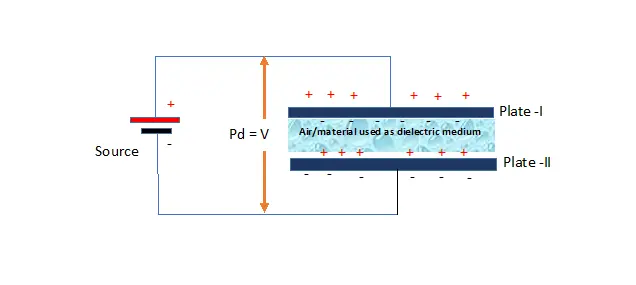
By keeping potential difference between plates constant, its charge has increased to considerable amount
Charge between plates when dielectric medium introduced (Q) = C/V
The capacitance value increased in insertion of die electric medium C =εA/d
Where is relative permittivity of dielectric medium
Relative permittivity of a dielectric medium defined as ratio of actual permittivity of a medium to absolute permittivity in vacuum
Relative permittivity εr = ε/ε0
It also known as dielectric constant of a material
It can be measured with and without dielectric medium by using proper experimental setup
It varies 1 to 10 for normal solid substances and more than 10 for liquid like alcohol and glycerin. For air it is more in high frequencies
The dielectric constant of a medium will be constant state, if medium does not vary from point to point. Definitely, at boundary between two medium dielectric constant changes and bodies are non-homogenous with respect to density and other properties are usually non homogenous with the dielectric constant as well
| Sl.No | Dielectric material | Dielectric constant | Dielectric strength 103 Volts per metre |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Paper | 3.7 | 16000 |
| 2 | Porcelain | 6 | 12000 |
| 3 | Silicon | 2.5 | 15000 |
| 4 | Teflon | 2.1 | 60000 |
| 5 | Vacuum | 1 | |
| 6 | Water | 80 | |
| 7 | Neoprine | 6.75T | 12000 |
| 8 | Bakelite | 4.9 | 34 |
| 9 | Wood | 3.34 | |
| 10 | Paper | 3.72 | 16000 |