1. What is Electric Current?
It is flow of electrons electric current through a medium such solid, liquid, gases.
2. What are the most important parts of an atom
An Atom has subdivided into two parts. They are Centre part act as nucleus. Orbit are extra nucleus part
3. Where Electrons are located?
Electrons are located in extra nucleus part of an atom. They are possessing in certain orbit as per 2n2 rule n= orbit number.
4. What are the sub particles available inside an atom?
Inside an atom proton and neutron available in nucleus, electrons are in orbit around nucleus
5. What kind of charges of an atom sub particles have?
Atom sub particles are proton, electrons, neutron
Protons – Positive charges
Electron – Negative Charges
Neutron- Does have any charges or it may be called as neutral charge.
6. What is charge?
Charge is termed as 1 coulomb, if a charged body has a positive charge which deficit of 6.25 x 1018 electrons. On other hand it has negative charge if there 6.25 x 1018 more electrons
7. What are the valance electrons?
In an atom of a metal body its last orbit contains valance electrons. Conductor have lot of valance electrons and insulators are not.
8. While electrons have more mobility?
Electrons are very less weight while comparing with protons 9.1093837015 × 10−31 kg. But protons have 1.6726 x 10-27 which is around 1837 times more than protons.
9. Why positive and negative charges are attracted each other?
A body is positive charge if it has deficiency electrons. On other hand it will be negatively charged if there more electrons. Hence to equalize or neutralize both charged particles it attract each other until both body charges become equal.
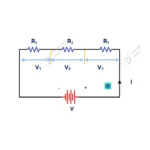
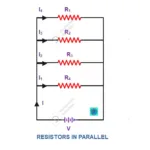
10. Definition of electric circuit?
A Electric circuit which consists source, load, controlling switches are connected to proper manner using conducting medium to utilize generated electrical energy from source which need to utilized in electrical load whenever it is required.
11.Brief Function of an Electric circuit components
1. Source – Generate electrical Energy
2. Switch – Control Flow of electric current
3. Load – Utilize generated electrical energy
3. Connecting medium – It transmit electrical energy from source wherever loads are connected.
12. What is Load? How it behaves?
A Load which utilizes electrical energy which generated from source. Almost are loads are resistive type. Which oppose flow of electrons through it. As there are restriction of flow of electrons it collides one another. It exhausted in form of heat. A load which convert electrical energy as per required form such heat, light, sound, force etc.
13. Define EMF?
EMF (Electro motive force ) is defined as it is offered by an electrical source to flow of electric current to circuit.
Unit of EMF is Volt.
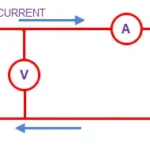
14. Define Pd
Pd (Potential Difference) is defined as it can be measured between any two point of an electrical circuit while current flowing though it.
15. Can we measure EMF while source delivering electric current?
No! We cannot measure EMF while circuit carrying electric current. Because it shows potential difference. It is important condition that source must be in open circuit and high resistance voltmeter to be used to measure EMF.
16. Copper and nichrome have both same length and same resistance. Which will be thicker?
Since resistivity of copper wire is less as compared to nichrome wire. So, to get equal resistance nichrome wire cross section will be more. Hence nichrome wire will be thicker,
17. Why manganin, nichrome, constantan alloy is used to make standard resistance?
Because they have more resistivity, we can make certain resistor using few amount alloys. Further its resistance almost does not change due to change of resistance.
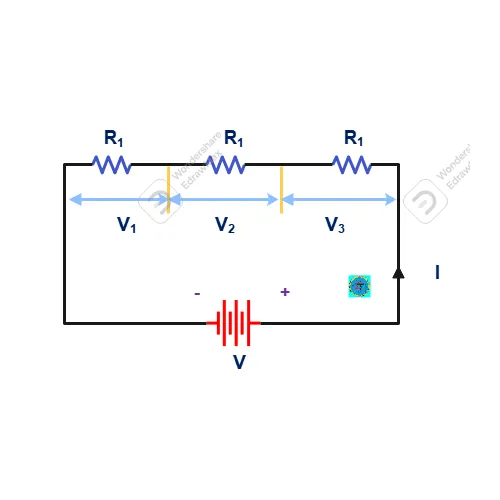
18. Define Ohms Law?
Ohms law defined while Current flowing through an electric circuit is directly proportional to applied voltage and inversely proportional to resistance offered by circuit while its physical and all other atmospheric conditions are remains unchanged.
19. Does Ohms law applicable to all circuit?
No! Ohms law applicable only where physical condition of circuits and atmospheric condition remains unchanged.
20. Can we verify Ohms law using a filament lamp?
A filament lamp is pure resistive type. But when it is glowing its temperature increases. So, lamp offers tow type of resistance such cold resistance and hot resistance. Hence physical condition of circuit changed. But it is most important that Voltage (V) and current (I) will be linear only if it is independent to changes in resistance.