Semiconductors Questions and Answers Part-I
1. Write definition of semiconductor?
Semiconductor is a material which conducting state is in between conductor and insulator. A semiconductor offer resistance to flow of electrons about 1×10-7 to 0.5 x 10-3 Ohm(Ω).
2. Example of semiconducting materials are used?
1. Silicon
2. Germanium
3. Corbon
4. Gallium arsenide
3. How a semiconductor material identified or Brief about its atomic structure
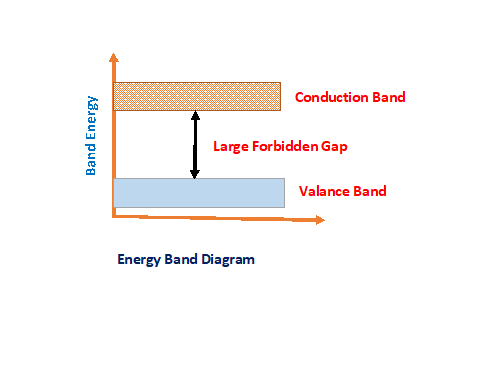
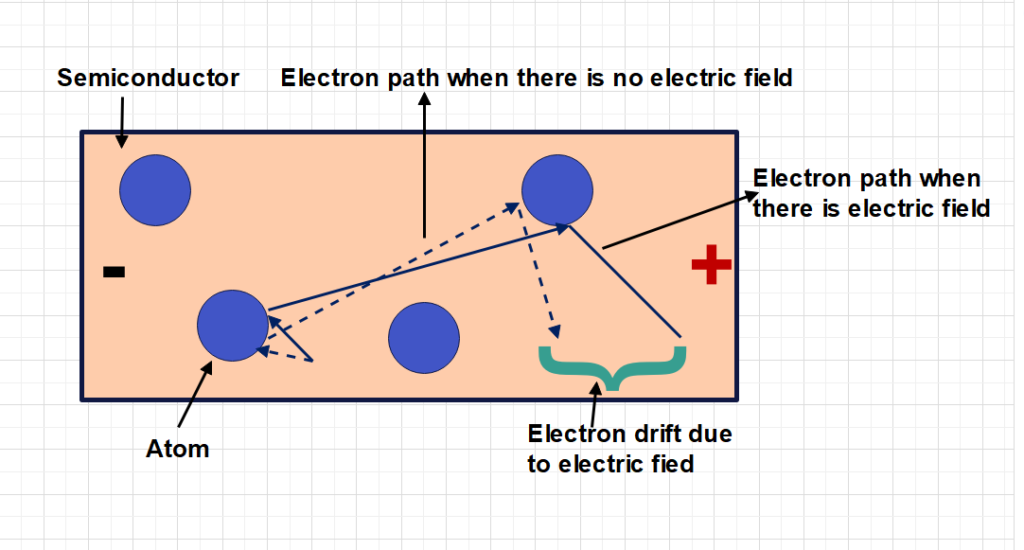
A semi conducting material last orbit contains valance electrons. These electrons are not strongly attached with nucleus. A very small force enough to detach it from its orbit. So, electrons are jumps to valance band to conduction band. Thereafter It starts to conduct electricity.
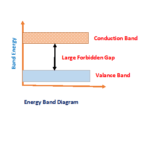
4. Energy gap or forbidden gap is required to bring electrons from valance band to conduction band in different semiconductor material.
For silicon = 1.3 eV,
For Germanium = 0.7 eV
5. While increase of temperature semi conductor’s resistivity also increases. Is it true?
No! All semiconductors are negative temperature co-efficient in nature. So, while increase of temperature its valance electrons jump from valance band to conduction band. It creates lot of free electrons which causes flow of electric current.
6. What is valance Band?
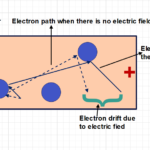
Valance band is defined as where electrons are located in orbit which bind with one another and nucleus . While apply external force these electrons can bring up to conduction band.
7. What is conduction band?
Conduction band termed as where electrons or occupied with higher energy levels . These electrons are more mobility. It can be moved direction by an external force.
8. What is forbidden gap?
It is an energy gap required electrons from valance band to conduction band
9. Does a semiconductor conduct electricity at room temperature?
No! At room temperature its valance electrons are made covalent bond with an adjacent atoms valance electron. Hence there is no free electrons. So, it does not conduct during room temperature.
10. What are the types of semiconductors?
There are two types of semiconductors
1. Intrinsic semiconductor (Pure Semiconductor)
2. Extrinsic semi-conductor
11. Why pure semiconductors are not used?
As all semiconductors atom made covalent band with its surrounding atom, there is very less charge carriers are available. Further it is more external voltage required to break co valent bond. So intrinsic semiconductors are not preferably used.
12. What is doping?
Doping is adding impurities to an intrinsic semi conducting material. By adding few numbers of impurities its conductivity increased.
13. How does a semiconductor called after doping done?
Doped semiconductor called as extrinsic semiconductors.
14. According to doping , classify semiconductors
Once doping done in an intrinsic semiconductor it is classified as below,
1. P- type semiconductor
2. N- type semiconductor
15.How a P-type semiconductors are made?
By Adding tri valent impurities such indium, gallium, aluminum, boron it shares 3 valance electrons with pure semiconductor. So, a hole has been created w.r.t each impurity atom after made co valent bond. No. of holes generated is depends on number of impurities added to it.
16. How a N- type semiconductors are made?
By Adding Penta valent impurities such phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, bismuth, it shares 5 valence electrons with pure semiconductor. So, there excess electron available made w.r.t each impurity of atom after made covalent bond. No. of atom generated is depends on number of impurities added to it.
17. With same degree of doping, why n-type semiconductor’s conductivity is more that p-type semiconductor?
As n-type semiconductor are having lot free electrons, whereas p-type are having holes. But electrons are more mobility than holes. Hence conductivity of n-type semiconductors is more .
18. Why Silicon material preferred over germanium?
Silicon has small leakage current while comparing with germanium.
19. State two application of semi conducting material
1. Fabrication of rectifier diodes
2. Fabrication of transistors
20. Examples of semi conducting devices
Rectifiers, Amplifiers, Oscillators etc.