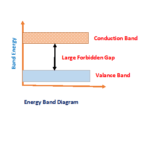
The conductivity in the semiconductor i.e current flowing though a semiconductor material is depending on two types of phenomena. This defines how semiconductor conducts electricity through it.
Types of conductivity in semiconductor
- Drift current
- Diffusion current
1.Drift Current
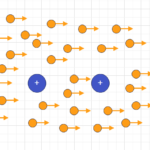
When electric field applied in free space, it will accelerate free electrons in a straight line. The free electron accelerated from negative point of the potential to the positive point of the same potential. Under ambient condition (let say as 25°C) , the potential applied between two points of the conductor or semiconductor, free electron available in the atom will be moved toward positive terminal under influence of the potential applied to it.
The electron flow will continue as long as potential available there. While flowing of these free electrons , it collides neighboring atom electrons also. Each time electrons collide neighboring atom or electrons , it drifts towards random direction. The electric field presence in that point maintain continues collision. But drifted direction definitely not towards positive point of electric potential. However, all electrons are reaching to Consequently ,current ,produced such way called as drift current. The drift current phenomenon happens in both conductors and semiconductors.
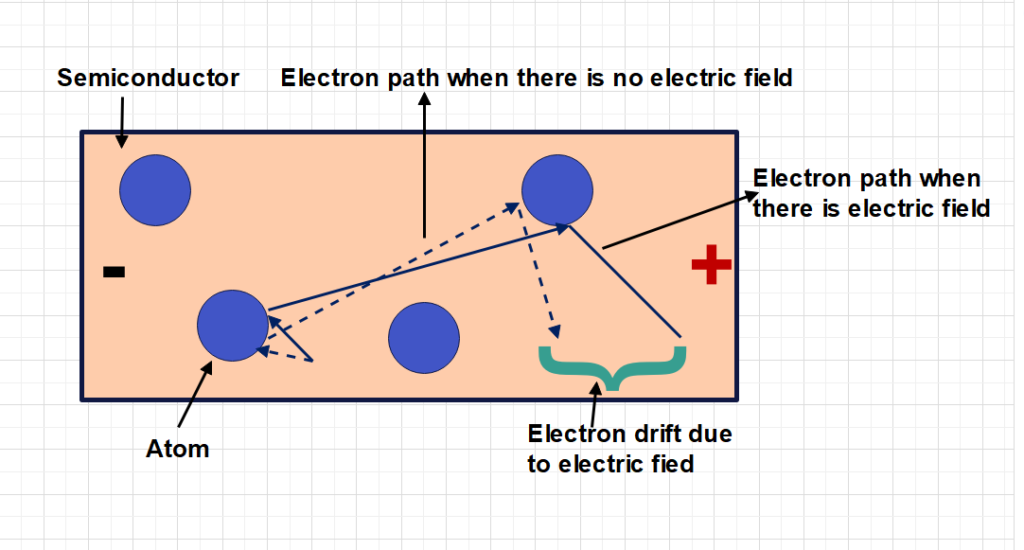
Charge carrier velocity in drift current
As we know that electrons are greater mobility than holes. Because holes are 1837 times more weight than electrons. The mobility constant determines the drift current under the influence of the electric field.
Velocity of the electrons vn = -μnE
Velocity of the holes vp = μpE
Where
μn, μp are electrons and holes mobility constant.
E is the electric field strength.
2. Diffusion Current
Diffusion current occurs when one end of the semiconductor material has concentrated charge carriers than other end, and same time external charge carrier penetrated from in same end by an external source, there are tow kind of activity are happening.
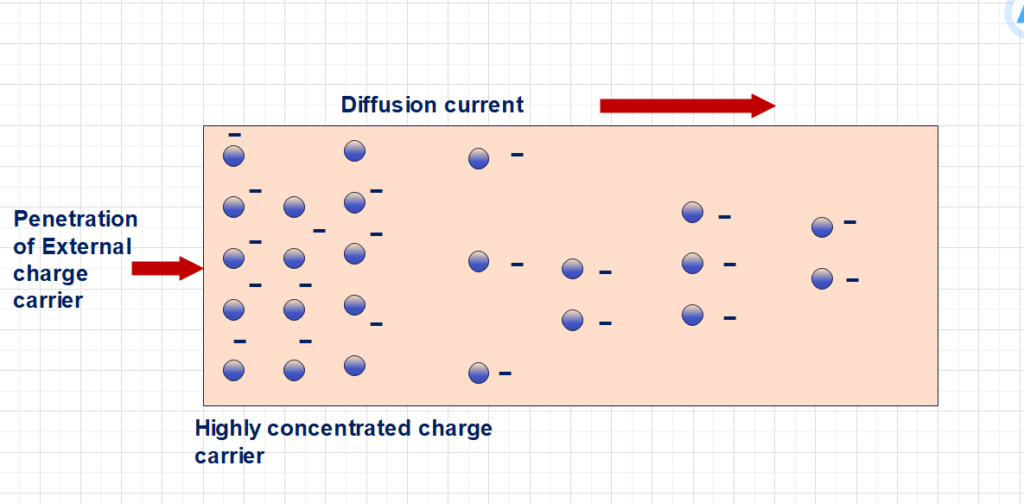
- Electrons- Hole pairing with opposite charge carries
- Repulsion force exerted between same carrier like electrons-electrons (or) holes-holes.
This produce tendency to move electrons gradually towards positive potential point. The diffusion of free electrons distributed from high concentrated area to low concentrated area in the semiconductor. Such movement of charge carrier constitutes electric current in the semiconductor. This type of current called as diffuse current.
These above both type conductivity in the semiconductor used to study about it